There are many software projects that start excellently but end up failing to deliver. This is due to lack of proper planning by software teams. Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a process that helps you build a product. Whether you are developing software, an enterprise system, or a mobile app, SDLC can help you structure an effective product. In this blog, we will help you learn the seven key phases of SDLC.
What is SDLC?
SDLC is a structured process that provides a step-by-step guide to developing software. It offers a clear framework for software development from the initial plan to final deployment. This process reduces the chances of ineffective use of resources and time. SDLC has seven key phases:
- Planning
- Requirements analysis,
- Design
- Development
- Testing
- Deployment
- Maintenance
Why is SDLC important?
SDLC is important for the following reasons:
- It helps inform all stakeholders about the development process
- It assists with cost estimation and risk management
- It results in efficient scheduling, planning, and execution
- It leads to better customer satisfaction
- It results in effective software delivery
The Seven Phases of SDLC
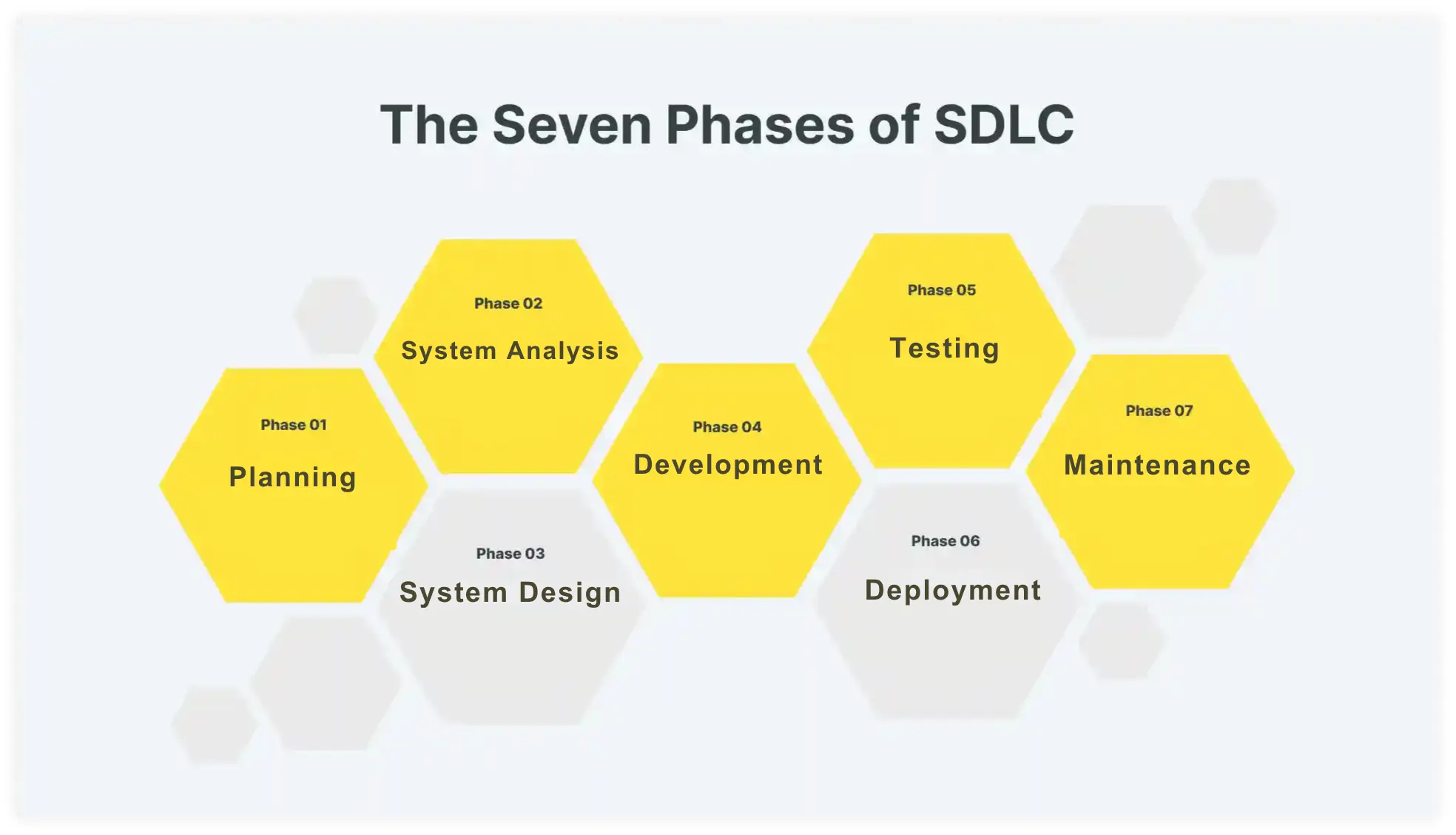
Planning
Planning is the first stage of SDLC. It is a stage where developers give an outline of their future product. They explain the challenges that the new product or feature will address. Development teams do not explain technical details such as which programming language will be used at this stage.
This stage only outlines the basic goals and challenges. They also identify any unrealistic goals that they may encounter in the future. For example, if a development team is building software and the company does not have the required budget, the team must convey this at the planning stage. This will ensure that the project does not halt at later stages. It also saves time and resources.
Requirement analysis
At this stage, development teams convert plans into actionable ideas. They perform technical analysis of the plans. They also outline all the functional and nonfunctional requirements. Development teams focus on specific features of the software at the analysis stage.
They engage all stakeholders to understand business needs and functional requirements. Business needs mean what the company requires and functional needs mean what the software needs to do to meet those requirements. At the end of this stage, the development team has requirement documentation which includes features, user interaction, and performance criteria for new software.
Design
The documentation developed at the previous stage acts as a reference for the development team to develop the architecture of the software. They provide a complete blueprint in which they outline the data flow, components, structure, and interfaces of the software.
The development team can present multiple designs in a Design Document Specification (DDS). These designs are reviewed by experts and market analysts. They choose the most logical and practical design for software development.
Development
This stage is also known as the coding or implementation stage. Based on the DDS, the development team starts developing the software. This can be a lengthy stage because the team writes the actual code.
The team performs front-end and back-end coding, configures system components, and integrates third-party services. Developers must use advanced tools, programming languages, and frameworks to develop software according to requirements.
Testing
At this stage, the development team tests the software. Every software is tested for these 4 things:
- Performance
- Usability
- Load
- Security
Development teams ensure that soft software functions according to requirements. They identify bugs and address them using bug tracking systems. There are four types of tests conducted by development teams. These include:
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- System testing
- User acceptance testing
Deployment
After successful tests, the company can decide to move on to the next stage of deployment. During this stage, the company decides to release the software product into the market to apply to the market.
Businesses may choose to roll out software in stages. They use tools like LaunchDarkly or ConfigCat to roll out software using feature flags, staged environments, or region-based toggles. This stage includes final preparations, configuration of servers, and data migration, to ensure that software remains compatible with the practical environment.
Maintenance
This is the final but continuous stage of software development. After deployment, the development teams continue reviewing the software to resolve any issues. Users can try the new software and report any bugs or errors missed during the testing phase.
This also includes rolling out new updates and providing technical post-launch support to users. Software maintenance helps to align software needs and market trends.
What are SDLC models?
There are a number of SDLC models that arrange stages of the Software Development Life Cycle in different ways. Following are a few top models:
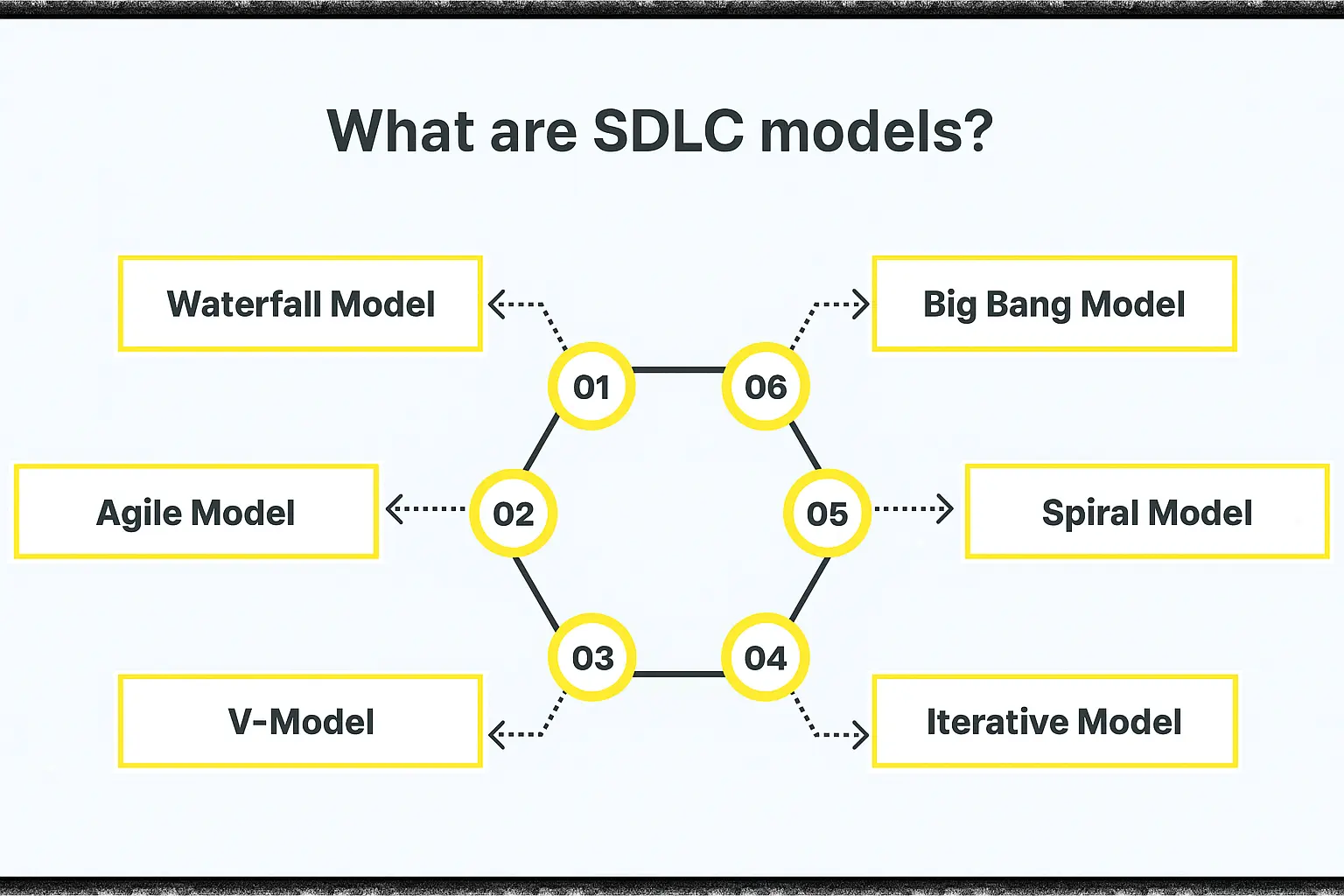
Waterfall model
In this mode, every stage starts only when the preceding stage is completed. It follows a linear approach and focuses on documentation and fixed requirements. The benefits of the waterfall model include:
- Clear structure
- Predictable budgets and timelines
- Suitable for projects where requirements do not change
Agile model
In this model, the development cycle is divided into several small stages called sprints. During these sprints, teams develop the software in small increments and adapt to changes developed over time. The benefits of using the agile mode:
- Flexibility to change
- Quick delivery of usable products
- Continuous collaboration with all stakeholders
- Continuous feedback and testing of the product
Iterative model
In this model, the team divides the software development stages into small repeatable cycles. It involves continuous development and refinement of products in repeated cycles. The benefits of using this model include:
- Continuous improvement
- Early user testing
- Reduced risks
Big Bang Methodology
This is a low-structure and high-risk approach. Here, developers directly start coding without any clear planning. The goal is to develop projects quickly. Therefore, it is not suitable for large projects. However, the benefits of this model include:
- Rapid development
- Minimum planning
- Flexibility to experiment freely
Spiral Model
This model is a combination of iterative and waterfall models. It is ideal for high-risk projects because it divides the project into smaller cycles. The pros of using a spiral model include:
- Prototyping before deployment
- Iterative improvements
- Allows for client feedback
V Model (Verification and Validation)
It is a version of the waterfall model. It focuses on testing at every stage. The development team tests and refines the product at every stage. The benefits of using this model include:
- Continuous improvement
- A decrease in risk
Conclusion
A high quality software product depends on a structured Software Development Life Cycle. It must follow all stages of SDLC including planning, requirements analysis, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance. These stages ensure that every step is aligned with the broader goal. If you want to enhance your software development, then explore Red Star Technologies and convert your idea into a successful product.